The Big Picture of Solar Energy’s Value
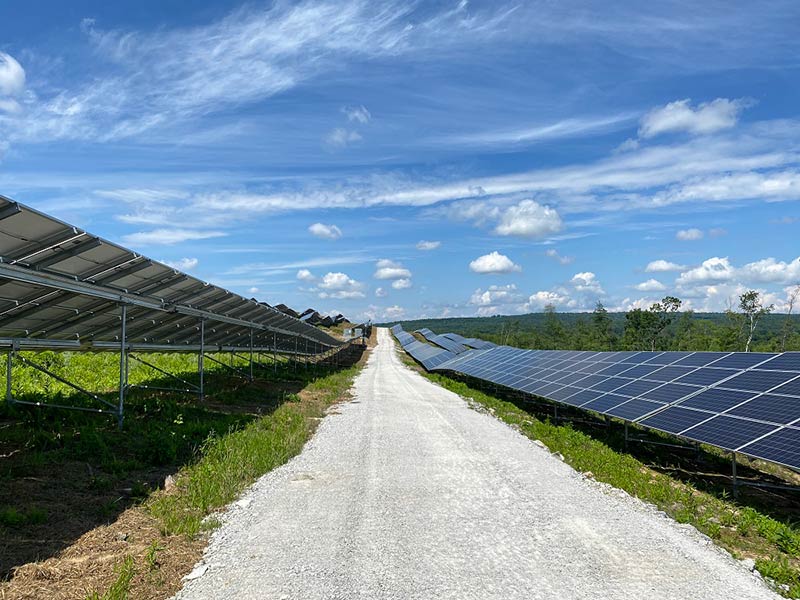

There have been thousands of studies trying to interpret the true value of solar. Some only look at benefits for the electric grid, or the cost savings to a home or business owner, but there is a multitude of areas significantly and directly impacted by solar. We considered all of these factors for a more holistic evaluation of the value of solar energy.
The Grid
Solar power is cheaper than fossil fuels. Generating solar power reduces the need for generation from central power plants and expensive peaker plants. This lowers peak charges from plants that produce power a few hours a year to reach peak demand and are a costly addition to electric bills year-round. Widespread use of solar energy systems would also increase price stability, as people would not be subject to variable energy costs.
Utilizing distributed solar generation, solar being more local opposed to central power plants, also limits line loss, as is travels shorter distances. Solar power and microgrids provide grid reliability and security as well. These grids are more complex to hack, easier to fix if they go down, and fewer outages occur when more localized, renewable microgrids and distributed generation can detach from others when necessary.
Society
Solar energy provides a great deal of intrinsic value to society, public health, and the environment that should be accounted for in analyzing the value of the energy generation source. For one, electric bills are far lower for consumers. Going solar can save families tens of thousands of dollars over the years. This allows people to be free from the volatility of electricity prices that increase nearly every year.
Secondly, using solar energy decreases CO2 and particulate matter that is released into the atmosphere that can cause health risks and preventable diseases. Diseases such as lung cancer, asthma, COPD, severe bronchitis, other respiratory issues, strokes, and cardiovascular problems can come from air pollution. The adoption of solar would replace the fossil fuels that cause so many health risks to society and especially sensitive groups. This would drastically lower peoples’ healthcare expenses and elongate life expectancies as well as improve the quality of life of everyone.

Solar is among the fastest-growing job markets in America. The solar industry alone provides more jobs than the entire fossil fuel industry in the United States. It is a growing field with the number of positions available steadily increasing. Electricity produced from solar only makes up about 1.6% of U.S. electricity generation, which means the local jobs and opportunities will continue to grow as the implementation of solar does. It is also an industry with minimal barriers to entry, that people from all different educational backgrounds can contribute to and be a part of the economic development.
Solar adds value to homes, which greatly benefits homeowners. A home with solar is expected to sell for on average 4.1% more than a comparable home without solar. Homes that have solar panels tend to sell faster than comparable homes without solar panels. This added value is when the solar system is purchased, a lease or power purchase agreement will not add value to a home as they are essentially just rented. Solar energy pays off within years after owning the system from the electricity savings, but if the owner plans to sell their home they see cash flow in that way as well.
Environment
Solar energy is a carbon-neutral energy source. This means when solar panels are used to produce electricity instead of fossil fuels, the air is cleaner and there is less pollution. “Distributed solar energy is on the rise, generating enough electricity to power more than 6 million homes each year, and resulting in annual carbon dioxide emission reductions equivalent to taking 4.4 million passenger vehicles off the road.”
Solar panels are recyclable as well. Not only can they generate power for around 30 years with no fuel source and no emissions, but their parts can be used again and again to continue clean energy production.
When solar is used instead of coal, it lowers CO2 emissions, sulfur dioxide, particulate matter, arsenic and more in the atmosphere that contributes to increased temperatures, acid rain and health risks from the combustion of coal as an energy source. It also reduces the need for dangerous coal mining jobs.

When solar is used to replace oil, it reduces CO2 emissions, oil spills, foreign conflict over oil and variable prices.
Natural gas produces less CO2 than coal and oil but produces methane, which is 34-86 times stronger than CO2 at trapping heat. Natural gas also emits nitrous oxide, sulfur, mercury, and particulates into the atmosphere. Eliminating the need for natural gas would also stop fracking, which is the process of extraction that contaminates groundwater, uses undisclosed and unregulated chemicals, has been thought to cause induced earthquakes, and disrupts ecosystems.
Natural gas has also caused deadly gas leaks in homes as well as explosions and fires – some of which hit really close to home for us. In September of 2018, natural gas caused leaks and explosions across the Merrimack Valley towns of Andover, North Andover, and Lawrence, MA which destroyed as many as 80 homes and buildings, injured dozens and caused a fatality to an 18-year old resident. Almost 9,000 people were displaced from their homes as Columbia gas tried to fix the issue.
There are numerous risks, chemicals, and pollutants that are directly from fossil fuel extraction, production, and even distribution. These pollutants, disasters, and costly finite resources can be avoided with renewable energy generation. The value of solar stretches further than many can calculate monetarily. The lives of coal miners, wildlife, and people’s right to clean air and water contribute to the value of solar: priceless.


